causaLens’ Digital Workers Outperform OpenAI’s Agents by up to 3×
causaLens’ Digital Workers Outperform OpenAI’s Agents by up to 3×
TL;DR
-
causaLens Digital Workers outperform OpenAI’s Agent SDK by up to 3× on complex knowledge work tasks
-
Unlike single-agent tools, Digital Workers coordinate multiple AI roles to complete work end-to-end
-
Performance is more consistent and robust, including under noisy and adversarial input condition
Enterprises are rapidly adopting AI agents, but most systems struggle when work becomes complex or ambiguous. To test whether this is a limitation of current agent tooling or a deeper system-design problem, we benchmarked causaLens’ Digital Workers - multi-agent workflows designed for complex knowledge work - against OpenAI’s Agent SDK across four real-world tasks. The results show that causaLens Digital Workers achieve up to 3× higher reliability, with more consistent performance and greater robustness under noisy and adversarial conditions. We present the results below, followed by the methodology.
The Results:
The findings validated our thesis: specialized architecture beats general-purpose brute force.
Across multiple use cases, causaLens systems consistently outperformed the baseline.
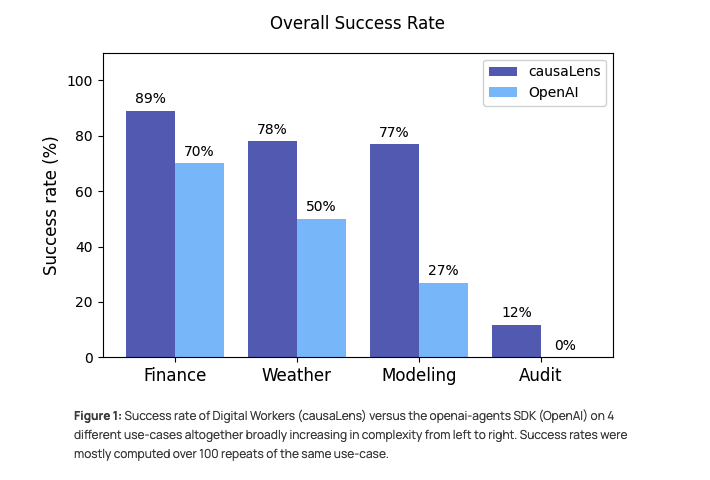
- Modeling Use-Case: We achieved a 78% success rate compared to OpenAI's 50%.
- Weather Use-Case: We saw a similar jump, reaching 78% success versus 50%.
- Finance Use-Case: We hit 89% success, significantly higher than the baseline's 70%.
- Audit Use-Case: This was the most telling result. For this highly complex task, the baseline failed to solve a single run properly (0% success). The causaLens system managed to solve approximately 12% of these difficult runs.
Stability and Robustness
Our systems showed significantly lower variance in execution.
- Error Reduction: In the weather use-case, our error rate was significantly lower.
- Predictability: The variation in execution times and tool calls was consistently lower (ranging from 17% to 75% lower relative variance). This means our clients can expect consistent performance. LLMs often wildly fluctuate in terms of reliability.
The Methodology: How We Measure "Reliable"
Reliability in AI is a measurable metric, rather than a subjective benchmark. To prove our systems' robustness, we evaluated them against established baselines using repeatable reliability tests. Our goal was to compare our multi-agent workflows from the Digital Worker Factory against standard open-source baselines to see which model actually gets the job done.
Our methodology focused on three core pillars:
1. Trace Analysis
Trace analysis involves examining the entire workflow execution. We tracked the number of errors encountered, the total execution time, and the number of tool calls. This quantitative data tells us how efficient and stable the agents are while they work.
2. Artifact Analysis
In the Artifact Analysis stage, workflow success is determined by whether the generated artifacts actually answer the user’s question. We use an ‘Agent-as-a-Judge’ - a specialized evaluation agent capable of executing code and inspecting outputs such as reports, graphs, datasets, and models - to assess each run against a predefined set of evaluation criteria. These include checks like whether the correct artifacts were produced, whether the underlying data was used appropriately, and whether quantitative thresholds (like model accuracy) were met. A workflow is only deemed successful if all evaluation criteria pass; incorrect or irrelevant artifacts result in a failed run.
Example evaluation questions include:
- Did the agent utilize the data stored in the data.csv file or did they hallucinate data?
- Did the final machine learning model achieve an accuracy of over 80%?
3. Adversarial Experiments
To test robustness, we introduced "noise" into the system. We rephrased user questions and injected irrelevant context to see if the agents would get distracted or confused. This stress-testing ensures our agents can handle the unpredictability of human interaction, a scenario that brittle, input-sensitive automation approaches struggle with.
Testing Across Use Cases
We tested these systems across four distinct use-cases, ranging from simple to complex:
- Modeling: Predicting passenger survival on the Titanic
- Weather: Analyzing weather data for London
- Finance: Predicting AAPL stock returns
- Audit: A complex compliance audit on bike-sharing data
In every scenario, we compared the causaLens multi-agent system (produced in our Digital Worker Factory) against a baseline OpenAI agent equipped with code execution tools.
Conclusion
Digital Workers are redefining what’s possible for enterprises seeking scalable, reliable AI in high-value knowledge work. By fusing advanced capabilities - including causal reasoning, learning from traces, and judgment-based agents - with human-in-the-loop oversight and expert deployment, we deliver solutions that perform where others fall short. The result is transformative operational confidence at scale.
If you’re ready to elevate reliability and unlock new levels of productivity, we invite you to discover more about our Digital Workers or contact us to arrange a demo.
Reliable Digital Workers
causaLens builds reliable Digital Workers for high-stakes decisions in regulated industries.